重度抑郁患者的脑组织形态学变化
2009-11-25 16:50:23 来源:丁香园 作者: 评论:0 点击:
Background: Neuroimaging studies have revealed structural and functional changes in brain regions associated with major depressive disorder (MDD). These abnormalities appear to be more common and extensive in patients with late-life depression than in younger patients.
It has therefore been hypothesized that different morphometric and pathological changes may be associated with MDD, depending on age.
背景:神经影像学研究发现重度抑郁症(MDD)患者脑组织存在功能和结构改变。相比早发患者,这种异常尤其在晚发终末期抑郁患者中更常见。由此可能涉及一个假说:重度抑郁症患者的形态和病理学可能与年龄存在关联。
Methods: This review stratifies the findings of the various studies on cell morphology in MDD according to age and assesses any possible differences in neuronal and glial cell changes in younger and older age groups.
方法:回顾关于重度抑郁症细胞形态学与年龄关系的相关文献,试图总结厘清早发和晚发患者中在神经元和胶质细胞方面的差异。
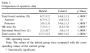
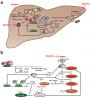
Results: Recent morphological studies in postmortem tissue have revealed alterations in neuron and glial cell populations in the frontal and subcortical circuitry associated with depression.
These may differ by age, with glial reduction consistently reported in younger groups in cortical areas and neuronal changes identified in studies with older subjects.
结果:近期发表的尸检形态学研究提示大脑额叶和皮质下通路的异常改变与抑郁有关。这种改变与发病年龄相关,早发型的患者以皮质区的胶质细胞持续减少有关,而晚发的患者主要表现为神经元的改变。
Conclusions: Apparent differences in the morphological changes between younger and elderly patients may suggest a differing pathological basis in MDD, dependent on age.
结论:早发和晚发患者在形态学上的显著差异提示重度抑郁症年龄依赖性的病理基础。
It has therefore been hypothesized that different morphometric and pathological changes may be associated with MDD, depending on age.
背景:神经影像学研究发现重度抑郁症(MDD)患者脑组织存在功能和结构改变。相比早发患者,这种异常尤其在晚发终末期抑郁患者中更常见。由此可能涉及一个假说:重度抑郁症患者的形态和病理学可能与年龄存在关联。
Methods: This review stratifies the findings of the various studies on cell morphology in MDD according to age and assesses any possible differences in neuronal and glial cell changes in younger and older age groups.
方法:回顾关于重度抑郁症细胞形态学与年龄关系的相关文献,试图总结厘清早发和晚发患者中在神经元和胶质细胞方面的差异。
Results: Recent morphological studies in postmortem tissue have revealed alterations in neuron and glial cell populations in the frontal and subcortical circuitry associated with depression.
These may differ by age, with glial reduction consistently reported in younger groups in cortical areas and neuronal changes identified in studies with older subjects.
结果:近期发表的尸检形态学研究提示大脑额叶和皮质下通路的异常改变与抑郁有关。这种改变与发病年龄相关,早发型的患者以皮质区的胶质细胞持续减少有关,而晚发的患者主要表现为神经元的改变。
Conclusions: Apparent differences in the morphological changes between younger and elderly patients may suggest a differing pathological basis in MDD, dependent on age.
结论:早发和晚发患者在形态学上的显著差异提示重度抑郁症年龄依赖性的病理基础。
相关热词搜索:
上一篇:产科静脉血栓(VTE)的预防及治疗
下一篇:GLP-1对胰岛β细胞功能的影响
频道总排行
频道本月排行
热门购物
评论排行
- 2011年临床执业医师考试实践技能真...(13)
- 腋臭手术视频(12)
- 2008年考研英语真题及参考答案(5)
- 节食挑食最伤女人的免疫系统(5)
- 核辐射的定义和单位(5)
- CKD患者Tm与IMT相关(5)
- 齐鲁医院普外科开展“喉返神经监护...(5)
- windows7激活工具WIN7 Activation v1.7(5)
- 正常微循环(5)
- 美大学性教育课来真的 男女上阵亲...(4)